
Take a look at the simple illustration of the range in the figure below.

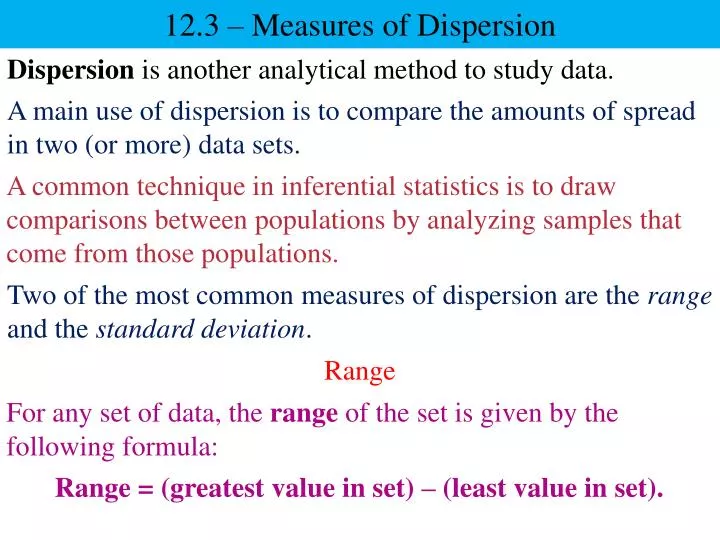
The formula for range would be read as the largest value minus the smallest value. This is the simplest possible of the absolute measures of dispersion and is defined as the difference between the largest and smallest values of the variable. The absolute measures of dispersion are as follows: Both relative and absolute measures of dispersion are useful to Six Sigma teams. They are used to compare the variation in two or more sets, which are having different units of measurements of observations.
#Name 3 measures of dispersio free
On the other hand, relative measures of dispersion are free from the units of the measurements of the observations. For example, when rainfall data is made available for different days in mm, any absolute measures of dispersion give the variation in rainfall in mm.
There are two types of measures of dispersion, namely:Ībsolute measures of dispersion indicate the amount of variation in a set of values in terms of units of observations. Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion Difference Small dispersion indicates high uniformity of the items, while large dispersion indicates less uniformity. The degree of variation is evaluated by various relative and absolute measures of dispersion. There is a difference or variation among the values.
#Name 3 measures of dispersio series
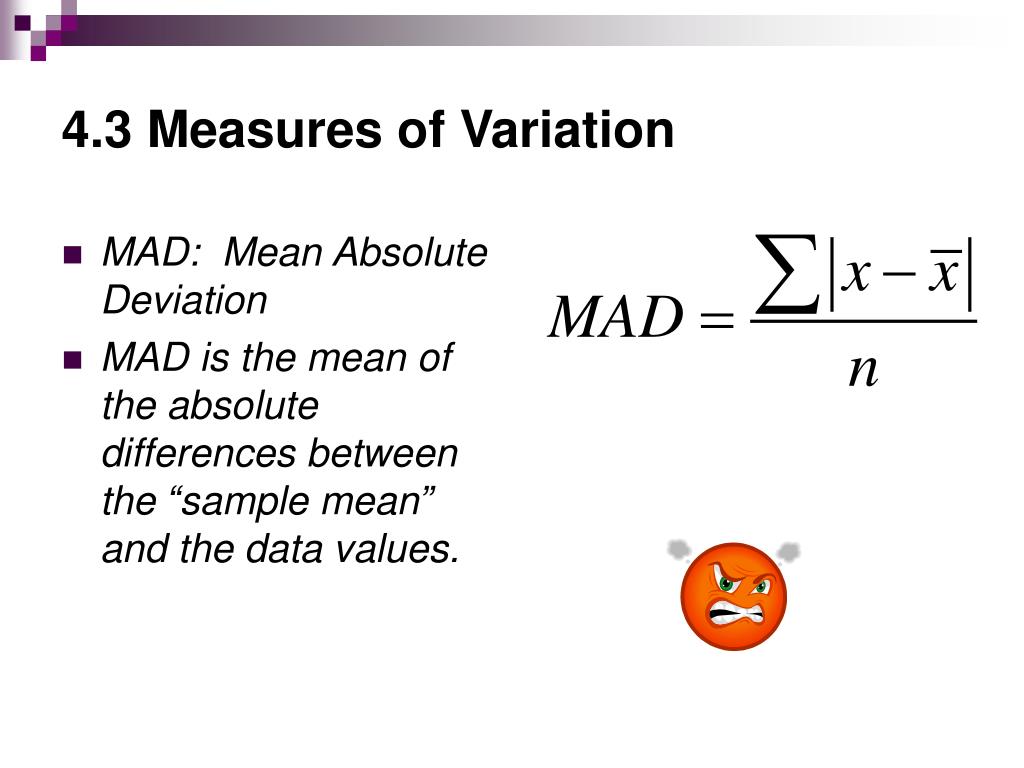
In a series of data, all the items or observations are not equal. Let’s have a detailed look at absolute measures of dispersion and how they are used in Six Sigma practices. It is a great way of showing how quantitative data is spread relative to the center point of the data.Īttend our 100% Online & Self-Paced Free Six Sigma Training. The word ‘Dispersion’ may also be used to indicate the spread of the data. The word ‘Dispersion’ refers to the lack of uniformity in the sizes or quantities of the items of a group or series of data. This characteristic of a frequency distribution is commonly referred to as ‘Dispersion’. To understand the spread of the data, Lean Six Sigma practitioners need to understand relative and absolute measures of dispersion. However, they do not reveal how the items are spread out on either side of the center. Measures of Central Tendency serve to locate the center of the distribution. In the Measure phase of the DMAIC process in Six Sigma, there are many types of statistical parameters that graduates of Lean Six Sigma Green Belt training or other Online Six Sigma courses should know.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
